Unlocking the Secrets of Cognition: The Powerful Role of Eye Movements in Assessment
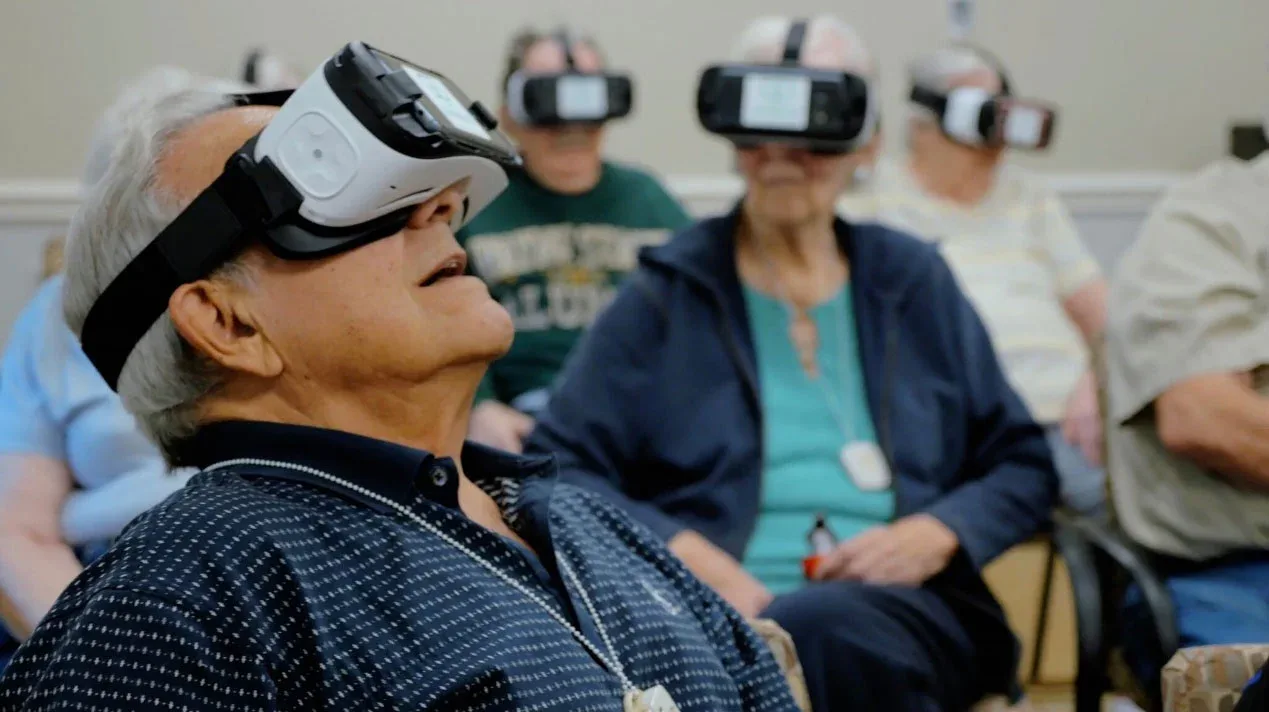
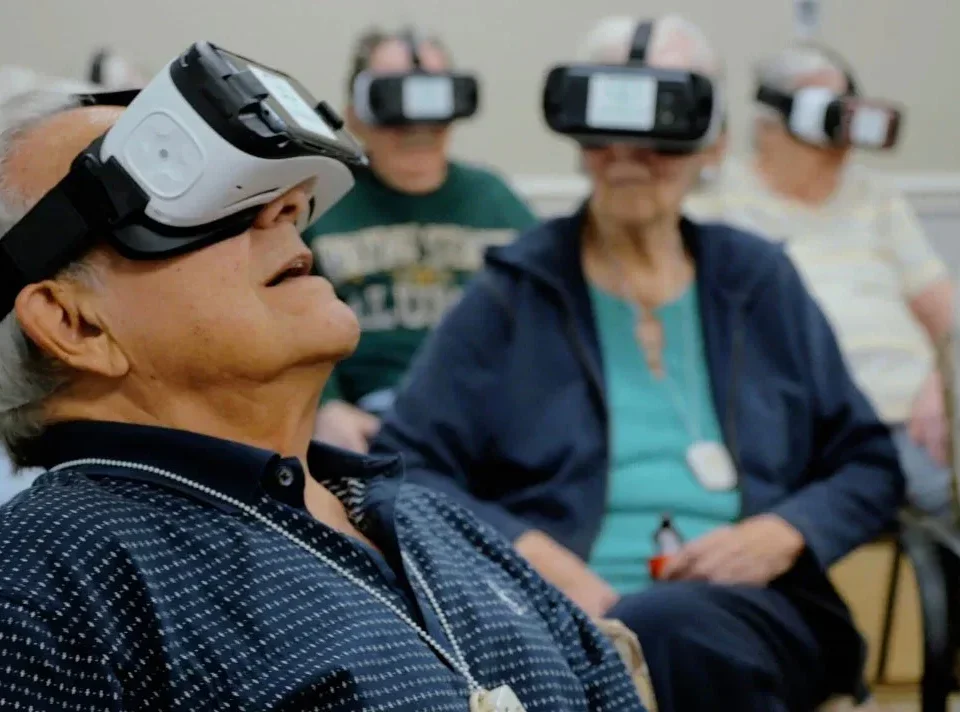
2024-12-17In recent years, the field of cognitive rehabilitation has seen a remarkable transformation with the emergence of virtual reality (VR) technologies. VR offers a powerful and immersive approach to addressing cognitive dysfunction, providing patients with engaging and customizable therapeutic experiences.
Cognitive dysfunction can arise from a variety of conditions, including traumatic brain injury, stroke, neurodegenerative diseases, and even normal aging. Traditionally, cognitive rehabilitation has relied on paper-and-pencil exercises or computer-based tasks, which can often feel tedious and disconnected from real-world experiences.
Virtual reality, on the other hand, allows patients to participate in simulated environments that closely mimic everyday situations. By engaging with virtual scenarios, individuals can practice and strengthen cognitive skills such as memory, attention, problem-solving, and executive function in a safe and controlled setting.
One of the key advantages of VR-based cognitive rehabilitation is the ability to tailor the virtual environment to the specific needs and abilities of the patient. Therapists can design customized tasks and challenges that target the individual’s cognitive deficits, while gradually increasing the complexity as the patient progresses.
Moreover, VR offers the opportunity for multimodal stimulation, incorporating visual, auditory, and even tactile feedback to create a more immersive and engaging experience. This multisensory approach has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize its connections in response to new experiences and learning.
Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of VR-based cognitive rehabilitation. For example, a recent randomized controlled trial found that patients with mild cognitive impairment who underwent VR-based training showed significant improvements in memory, attention, and executive function compared to those receiving traditional cognitive therapy.
As VR technology continues to advance, the potential for its application in cognitive rehabilitation is vast.
Enhancing Neuroplasticity and Learning
One of the key benefits of VR-based cognitive therapy is its ability to harness the brain’s remarkable capacity for neuroplasticity. By providing highly engaging and interactive virtual experiences, VR can stimulate the brain to form new neural pathways and strengthen existing connections. This neuroplasticity is essential for improving cognitive function and facilitating the relearning of skills impaired by injury or disease.
Increased Motivation and Engagement
Traditional cognitive rehabilitation techniques can often feel monotonous and demotivating for patients. Virtual reality, on the other hand, offers a level of immersion and interactivity that can significantly enhance patient engagement and motivation. By creating enjoyable and challenging virtual environments, VR-based therapies can encourage patients to actively participate in their rehabilitation, leading to better outcomes and higher rates of adherence.
Personalized and Adaptive Rehabilitation
VR platforms allow for the development of highly customized rehabilitation programs tailored to the unique needs and abilities of each patient. Therapists can design virtual scenarios that target specific cognitive deficits, adjust task difficulty, and provide real-time feedback to facilitate progress. This level of personalization is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation, as each individual’s cognitive profile and rehabilitation needs are unique.
Integration with Assistive Technologies
The combination of VR with other emerging technologies, such as brain-computer interfaces and wearable sensors, can further enhance the capabilities of cognitive rehabilitation. By monitoring patients’ brain activity, physiological responses, and behavioral patterns, these integrated systems can provide valuable insights into the patient’s cognitive processes and inform the development of more effective VR-based interventions.
Ecological Validity and Real-World Transfer
One of the limitations of traditional cognitive rehabilitation approaches is the lack of ecological validity, meaning the exercises may not adequately reflect the cognitive demands of real-world situations. Virtual reality, however, can create simulated environments that closely mimic everyday scenarios, allowing patients to practice and develop skills that are directly applicable to their daily lives. This transfer of learning from the virtual to the real world is a crucial aspect of successful cognitive rehabilitation.
As the field of VR-based cognitive rehabilitation continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective approaches emerge. With the ability to create immersive, personalized, and technologically advanced therapeutic experiences, virtual reality holds great promise for revolutionizing the way we approach cognitive rehabilitation and empowering individuals on their path to cognitive recovery and improved quality of life.