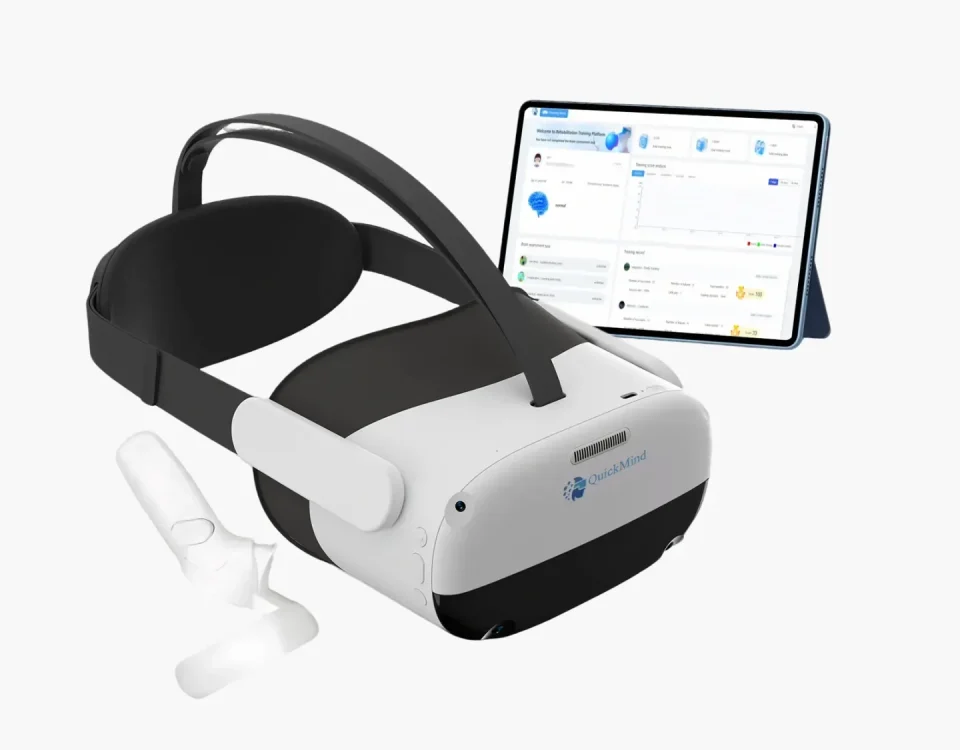
Revolutionizing Alzheimer’s Care: How Virtual Reality is Transforming the Landscape
2024-12-17
Unlocking the Power of Your Cognitive Function
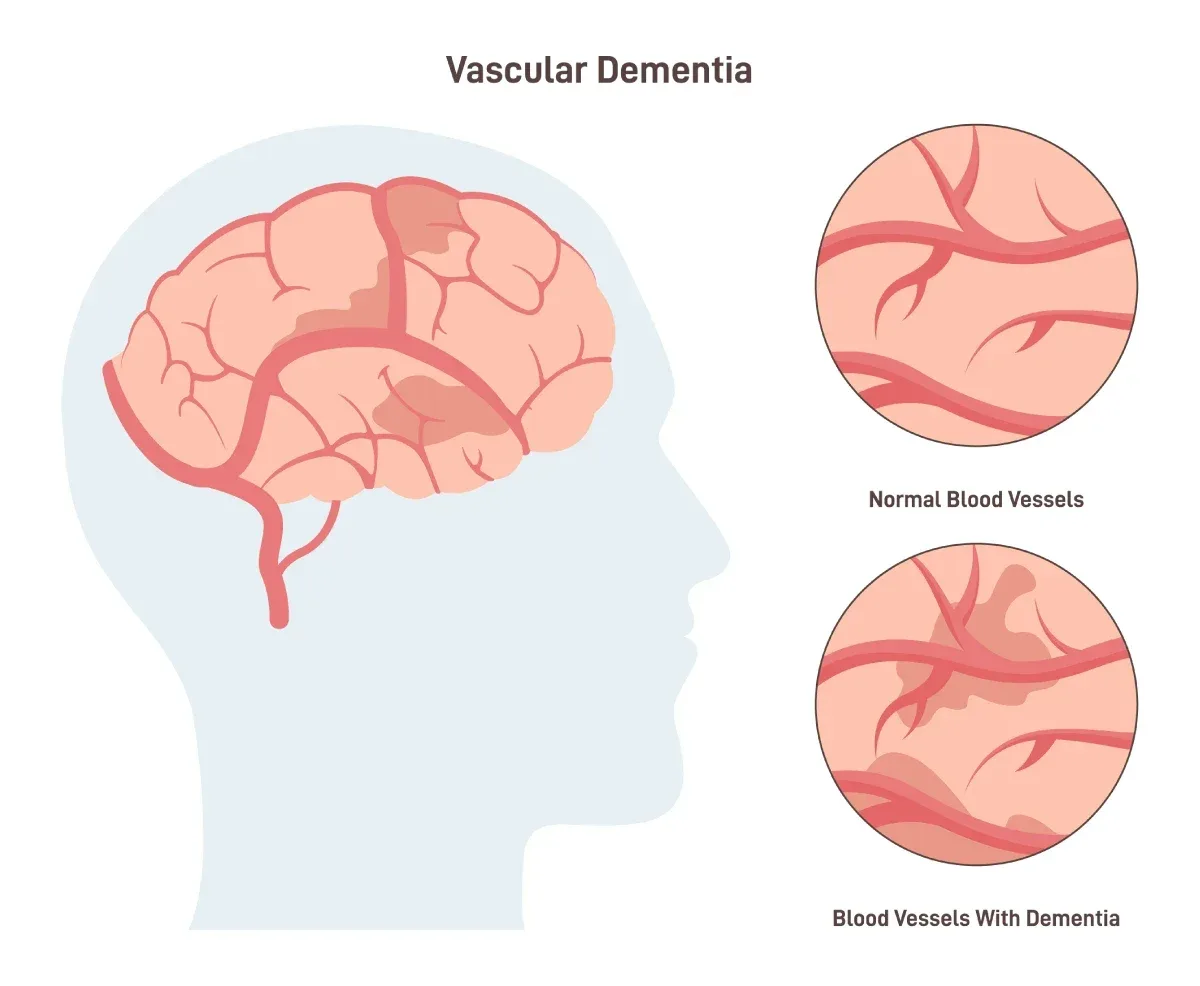
2024-12-17Vascular dementia is a type of cognitive impairment that results from damage to the blood vessels in the brain. This damage can be caused by a stroke, series of small strokes, or other conditions that restrict blood flow to the brain. As a result, people with vascular dementia experience a decline in their thinking, reasoning, and memory skills.
Symptoms of Vascular Dementia
The symptoms of vascular dementia can vary depending on the location and extent of the brain damage, but common signs include:
- Difficulty with planning, problem-solving, and organizing thoughts
- Slower processing speed and information processing
- Problems with attention, concentration, and memory
- Unsteady gait and coordination issues
- Mood changes, such as depression or apathy
- Difficulty completing daily tasks and self-care
- These symptoms often develop suddenly after a stroke or progress
in a step-wise fashion as additional strokes occur.
Causes of Vascular Dementia
The primary cause of vascular dementia is reduced blood flow to the brain, which can be the result of:
- Strokes, either large or a series of small strokes
- Diseases that damage blood vessels, such as atherosclerosis
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Lifestyle factors that increase the risk of vascular problems, such as an unhealthy diet and lack of exercise, can also contribute to the development of vascular dementia.
Managing Vascular Dementia
There is no cure for vascular dementia, but there are ways to manage the condition and potentially slow its progression:
Treating underlying conditions: Controlling risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can help prevent further damage to the brain’s blood vessels.
Rehabilitation: Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help maintain daily living skills and improve quality of life.
Cognitive training: Exercises that challenge the brain may help preserve cognitive function.
Medication: Certain medications may be prescribed to treat specific symptoms, such as mood changes or coordination issues.
Lifestyle changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and cognitive stimulation can all support brain health.
While vascular dementia can be a difficult diagnosis, understanding the condition and taking steps to manage it can help individuals maintain their independence and quality of life for as long as possible.